Redux is a predictable state management library that helps manage global state in React applications. In this blog, we’ll go through the core concepts of Redux and how to set it up in a React project.
1. Core Concepts of Redux
Redux revolves around a few key principles that make state management predictable and maintainable.
Single Source of Truth
The entire state of an application is stored in a single object tree inside a Redux store.
State is Read-Only
State can only be modified by dispatching actions. This ensures predictable updates and avoids direct mutations.
Changes are Made with Pure Functions
Reducers specify how state changes in response to actions. They must be pure functions, meaning they return a new state without modifying the existing state.
2. Setting Up Redux in a React Application
To use Redux in a React project, install the necessary dependencies:

Creating a Redux Store
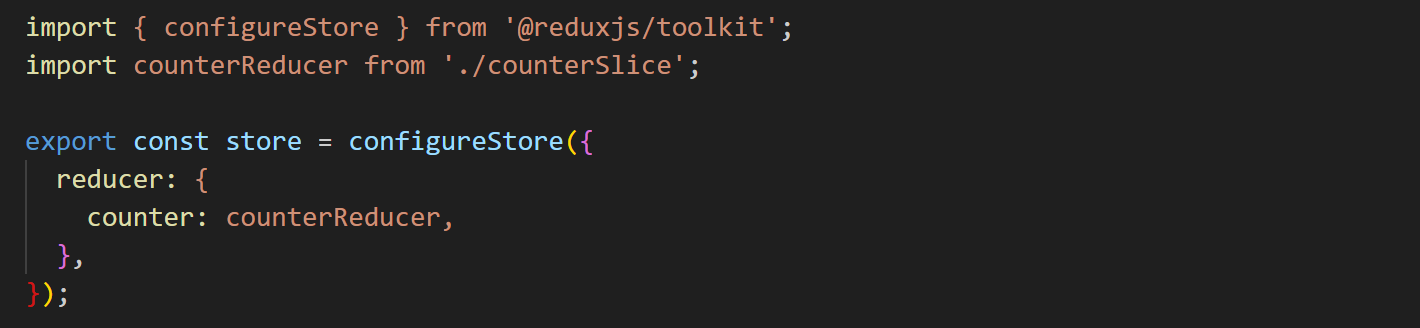
This sets up a Redux store using configureStore from Redux Toolkit.
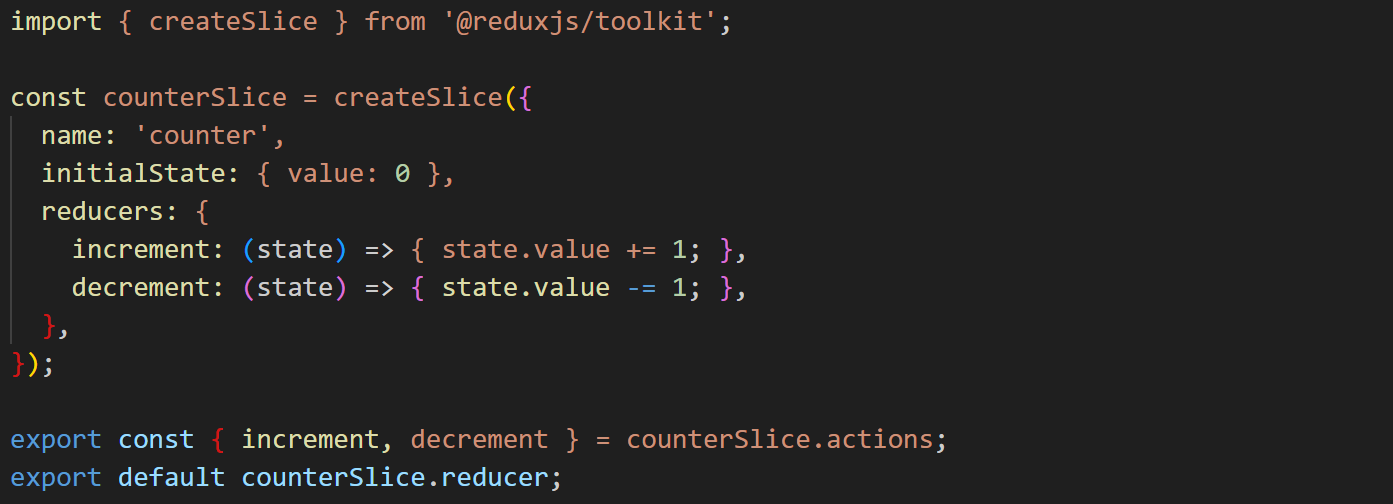
Creating a Slice
A slice contains a reducer and associated actions.
Providing the Store to React
To connect Redux with React, wrap the application in a Provider:
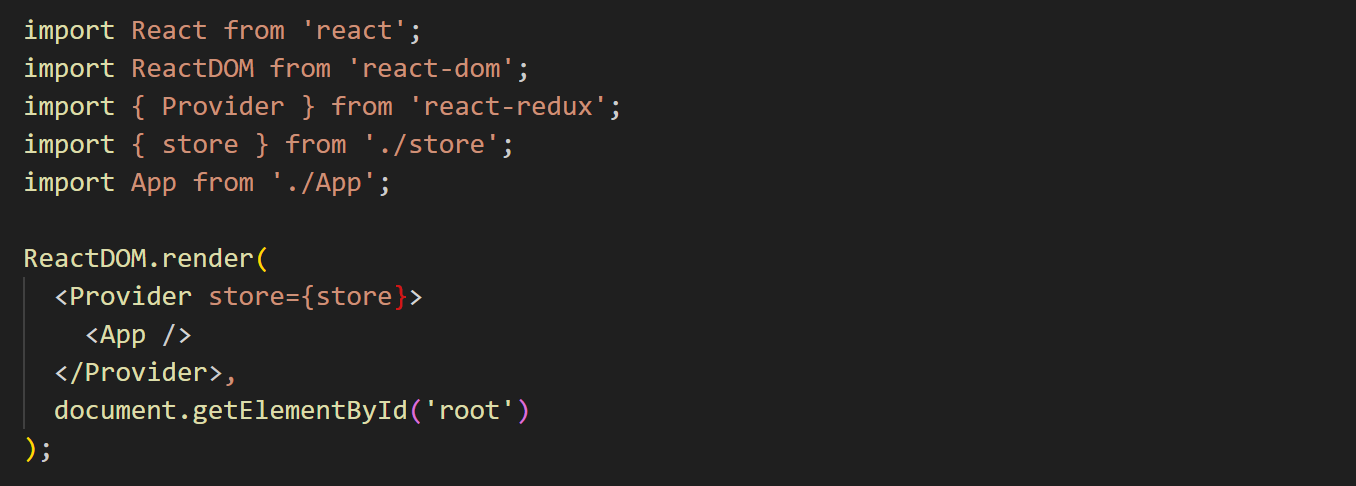
This allows any component in the app to access the Redux store.
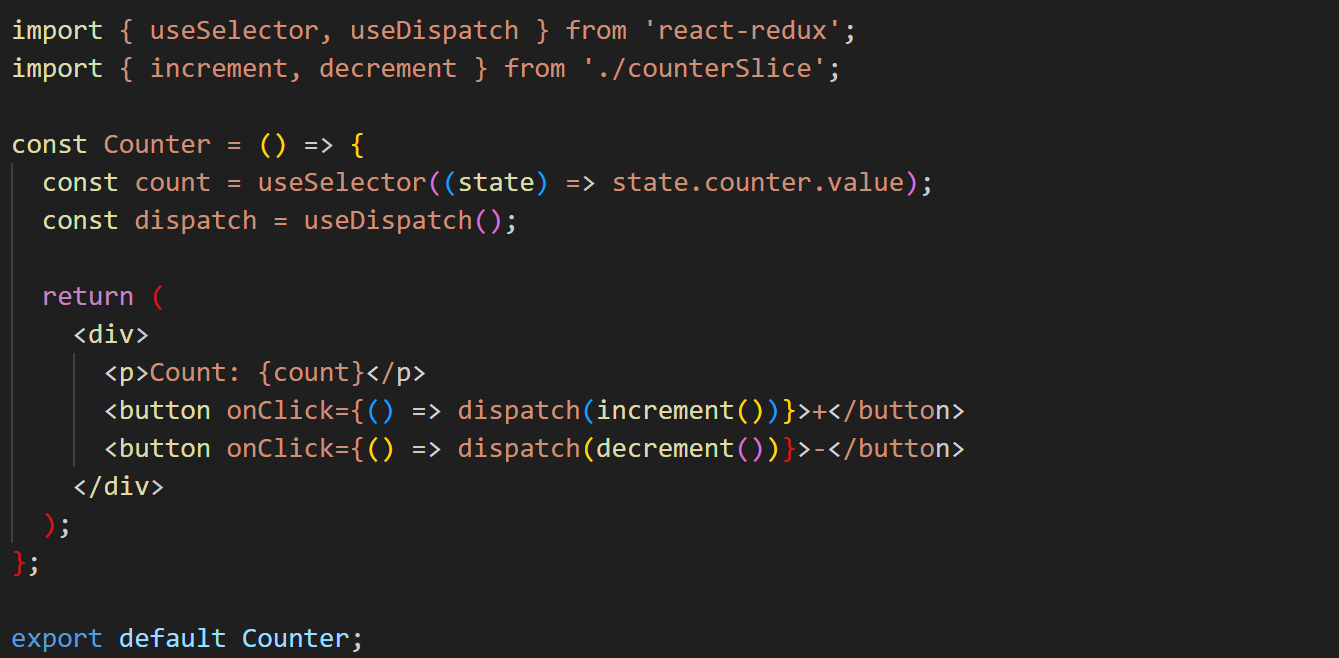
3. Using Redux State in Components
To read and update Redux state, use useSelector and useDispatch from React Redux.
Conclusion
Redux provides a predictable way to manage state in large applications. By understanding its core principles and setting up Redux Toolkit, developers can simplify state management in React projects. In the next blog, we’ll explore Understanding Actions, Reducers, and Middleware in Redux to dive deeper into handling state changes efficiently. has context menu
