Problem Statement:
The HR department needs a report where users can select a single department from a slicer to view specific details, such as the average salary or headcount for that department. If multiple departments are selected, the report should show a generic message or summary data. If no department is selected, it should display the overall average salary across all departments.
Why SELECTEDVALUE is the Solution:
- In this scenario, SELECTEDVALUE {Syntax: SELECTEDVALUE (<columnName> [, <alternateResult>]) is well-suited because:
- It returns the selected department when only one is chosen, which can be used directly in calculations or as dynamic text in report titles.
- It allows you to define alternative results (e.g., a fallback message or default value) if multiple or no selections are made, making it adaptable and user-friendly.
DAX Example:
To display the selected department name or show "All Departments" when multiple or no departments are selected, you could use:
DAX:
Use Case 1: Selected_Department = SELECTEDVALUE(Departments[DepartmentName], "All Departments")
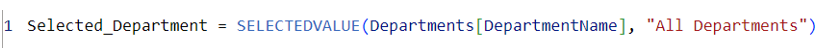
For a dynamic measure that calculates the average salary based on the selected department, you could write:
Use Case 2: Average_Salary_by_Department = CALCULATE(AVERAGE(Employee[Salary]), FILTER(Employee, Employee[Department] = SELECTEDVALUE(Departments[DepartmentName])))

This will:
- Return the average salary for the selected department,
- Show the overall average if no department or multiple departments are selected.
Key Point:
SELECTEDVALUE is ideal when you want to retrieve a single selected value and provide a fallback for other cases, such as creating dynamic headers, labels, or conditional calculations in response to slicer selections.
